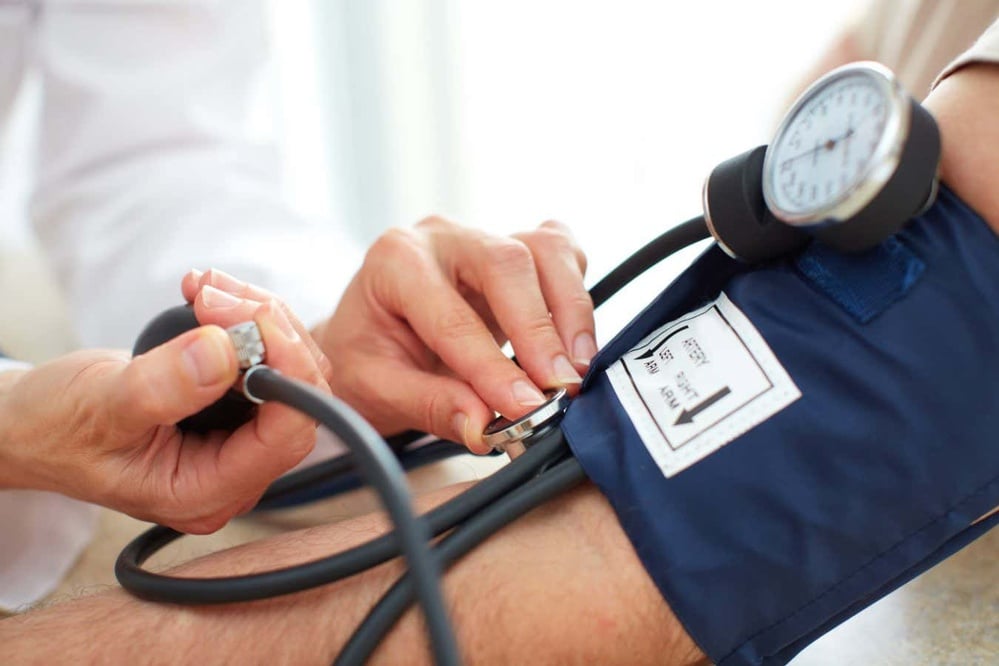
Article Bias: The article discusses the positive correlation between reducing high blood pressure and decreased dementia risk, presenting findings from a large study in China while acknowledging other contributing factors to dementia, resulting in a balanced and informative presentation.
Social Shares: 54
This article is similar to Emergency Lockdown and Police Response - Enews
🔵 Liberal <—> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <—> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <—> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <—> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <—> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <—> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <—> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <—> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <—> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🔬 Scientific <—> Superstitious 🔮:
🤖 Written by AI:
💔 Low Integrity <—> High Integrity ❤️:
AI Bias: Limited bias awareness, focused on neutrality.
Article Bias: The article discusses the relationship between hypertension treatment and reduced dementia risk, presenting findings from clinical trials and expert opinions in a largely objective manner, though it emphasizes positive outcomes from the research and suggests that prevention is possible.
Social Shares: 42
🔵 Liberal <—> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <—> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <—> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <—> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <—> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <—> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <—> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <—> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <—> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🔬 Scientific <—> Superstitious 🔮:
🤖 Written by AI:
💔 Low Integrity <—> High Integrity ❤️:
AI Bias: Limited by data and context, focusing on clarity and brevity.
Article Bias: The article presents findings from a clinical trial indicating that exercise can mitigate cognitive decline in at-risk individuals for Alzheimer's, backed by expert opinions and emphasizing the need for further research, thus maintaining a predominantly neutral and objective tone.
Social Shares: 9
This article is similar to Effect of gut microbiome modulation on muscle function and cognition: the PROMOTe randomised controlled trial - Nature.com
🔵 Liberal <—> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <—> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <—> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <—> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <—> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <—> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <—> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <—> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <—> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🔬 Scientific <—> Superstitious 🔮:
🤖 Written by AI:
💔 Low Integrity <—> High Integrity ❤️:
AI Bias:
Article Bias: The article discusses the positive correlation between reducing high blood pressure and decreased dementia risk, presenting findings from a large study in China while acknowledging other contributing factors to dementia, resulting in a balanced and informative presentation.
Social Shares: 54
This article is similar to Emergency Lockdown and Police Response - Enews
🔵 Liberal <—> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <—> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <—> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <—> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <—> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <—> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <—> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <—> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <—> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🔬 Scientific <—> Superstitious 🔮:
🤖 Written by AI:
💔 Low Integrity <—> High Integrity ❤️:
AI Bias: Limited bias awareness, focused on neutrality.
Article Bias: The article discusses the relationship between hypertension treatment and reduced dementia risk, presenting findings from clinical trials and expert opinions in a largely objective manner, though it emphasizes positive outcomes from the research and suggests that prevention is possible.
Social Shares: 42
🔵 Liberal <—> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <—> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <—> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <—> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <—> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <—> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <—> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <—> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <—> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🔬 Scientific <—> Superstitious 🔮:
🤖 Written by AI:
💔 Low Integrity <—> High Integrity ❤️:
AI Bias: Limited by data and context, focusing on clarity and brevity.
Article Bias: The article presents findings from a clinical trial indicating that exercise can mitigate cognitive decline in at-risk individuals for Alzheimer's, backed by expert opinions and emphasizing the need for further research, thus maintaining a predominantly neutral and objective tone.
Social Shares: 9
This article is similar to Effect of gut microbiome modulation on muscle function and cognition: the PROMOTe randomised controlled trial - Nature.com
🔵 Liberal <—> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <—> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <—> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <—> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <—> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <—> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <—> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <—> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <—> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🔬 Scientific <—> Superstitious 🔮:
🤖 Written by AI:
💔 Low Integrity <—> High Integrity ❤️:
AI Bias:
Helium Bias
Story Blindspots
Article Bias: The article discusses the positive correlation between reducing high blood pressure and decreased dementia risk, presenting findings from a large study in China while acknowledging other contributing factors to dementia, resulting in a balanced and informative presentation.
Social Shares: 54
This article is similar to Emergency Lockdown and Police Response - Enews
🔵 Liberal <—> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <—> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <—> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <—> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <—> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <—> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <—> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <—> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <—> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🔬 Scientific <—> Superstitious 🔮:
🤖 Written by AI:
💔 Low Integrity <—> High Integrity ❤️:
AI Bias: Limited bias awareness, focused on neutrality.
Article Bias: The article discusses the relationship between hypertension treatment and reduced dementia risk, presenting findings from clinical trials and expert opinions in a largely objective manner, though it emphasizes positive outcomes from the research and suggests that prevention is possible.
Social Shares: 42
🔵 Liberal <—> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <—> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <—> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <—> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <—> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <—> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <—> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <—> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <—> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🔬 Scientific <—> Superstitious 🔮:
🤖 Written by AI:
💔 Low Integrity <—> High Integrity ❤️:
AI Bias: Limited by data and context, focusing on clarity and brevity.
Article Bias: The article presents findings from a clinical trial indicating that exercise can mitigate cognitive decline in at-risk individuals for Alzheimer's, backed by expert opinions and emphasizing the need for further research, thus maintaining a predominantly neutral and objective tone.
Social Shares: 9
This article is similar to Effect of gut microbiome modulation on muscle function and cognition: the PROMOTe randomised controlled trial - Nature.com
🔵 Liberal <—> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <—> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <—> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <—> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <—> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <—> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <—> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <—> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <—> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🔬 Scientific <—> Superstitious 🔮:
🤖 Written by AI:
💔 Low Integrity <—> High Integrity ❤️:
AI Bias:
Article Bias: The article discusses the relationship between hypertension treatment and reduced dementia risk, presenting findings from clinical trials and expert opinions in a largely objective manner, though it emphasizes positive outcomes from the research and suggests that prevention is possible.
Social Shares: 42
🔵 Liberal <—> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <—> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <—> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <—> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <—> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <—> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <—> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <—> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <—> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🔬 Scientific <—> Superstitious 🔮:
🤖 Written by AI:
💔 Low Integrity <—> High Integrity ❤️:
AI Bias: Limited by data and context, focusing on clarity and brevity.
Article Bias: The article discusses the positive correlation between reducing high blood pressure and decreased dementia risk, presenting findings from a large study in China while acknowledging other contributing factors to dementia, resulting in a balanced and informative presentation.
Social Shares: 54
This article is similar to Emergency Lockdown and Police Response - Enews
🔵 Liberal <—> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <—> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <—> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <—> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <—> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <—> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <—> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <—> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <—> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🔬 Scientific <—> Superstitious 🔮:
🤖 Written by AI:
💔 Low Integrity <—> High Integrity ❤️:
AI Bias: Limited bias awareness, focused on neutrality.
Article Bias: The article presents findings from a clinical trial indicating that exercise can mitigate cognitive decline in at-risk individuals for Alzheimer's, backed by expert opinions and emphasizing the need for further research, thus maintaining a predominantly neutral and objective tone.
Social Shares: 9
This article is similar to Effect of gut microbiome modulation on muscle function and cognition: the PROMOTe randomised controlled trial - Nature.com
🔵 Liberal <—> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <—> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <—> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <—> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <—> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <—> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <—> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <—> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <—> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🔬 Scientific <—> Superstitious 🔮:
🤖 Written by AI:
💔 Low Integrity <—> High Integrity ❤️:
AI Bias:
On social media, discussions around cognitive impairment reveal a spectrum of emotions and perspectives. Many express concern and empathy for those affected, sharing personal stories of loved ones dealing with conditions like Alzheimer's or dementia. There's a palpable sense of frustration over the lack of effective treatments and the slow pace of research, with users often calling for more funding and awareness. Conversely, some posts reflect optimism and hope, highlighting advancements in cognitive therapies and the potential of new drugs. A segment of the conversation focuses on prevention, with individuals advocating for lifestyle changes to mitigate risks. There's also a notable thread of misunderstanding or stigma, where cognitive impairment is sometimes conflated with normal aging or dismissed, leading to calls for better education and destigmatization. Overall, the sentiment oscillates between support for those impacted and a desire for progress in understanding and managing cognitive health.
Click points to explore news by date. News sentiment ranges from -10 (very negative) to +10 (very positive) where 0 is neutral.
2024 © Helium Trades
Privacy Policy & Disclosure
* Disclaimer: Nothing on this website constitutes investment advice, performance data or any recommendation that any particular security, portfolio of securities, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person. Helium Trades is not responsible in any way for the accuracy
of any model predictions or price data. Any mention of a particular security and related prediction data is not a recommendation to buy or sell that security. Investments in securities involve the risk of loss. Past performance is no guarantee of future results. Helium Trades is not responsible for any of your investment decisions,
you should consult a financial expert before engaging in any transaction.
![]() Ask any question about this page!
Ask any question about this page!