Article Bias: The article provides a factual account of Typhoon Bebinca and its impact in China, emphasizing the official reports on casualties, evacuation efforts, and the storm's progression without showcasing opinion or sensationalism.
Social Shares: 0
🔵 Liberal <-> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <-> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <-> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <-> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <-> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <-> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <-> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <-> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <-> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🤖 Written by AI:
AI Bias: Objective but limited by a focus on current events.
Article Bias: The article provides an informative report on Typhoon Bebinca and its impacts, including forecasts and historical context, without exhibiting strong biases, though it mentions scientific links to climate change.
Social Shares: 0
🔵 Liberal <-> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <-> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <-> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <-> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <-> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <-> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <-> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <-> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <-> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🔬 Scientific <-> Superstitious 🔮:
🤖 Written by AI:
AI Bias: Limited by training data, may not fully capture nuances.
Article Bias: The article presents a straightforward account of Tropical Storm Pulasan's trajectory and impact on Shanghai and Japan, focusing on factual information without presenting any clear bias or sensationalism; it adequately informs readers about the risks associated with the storm while delineating its physical effects in a clear and objective manner.
Social Shares: 83
🔵 Liberal <-> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <-> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <-> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <-> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <-> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <-> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <-> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <-> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <-> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🤖 Written by AI:
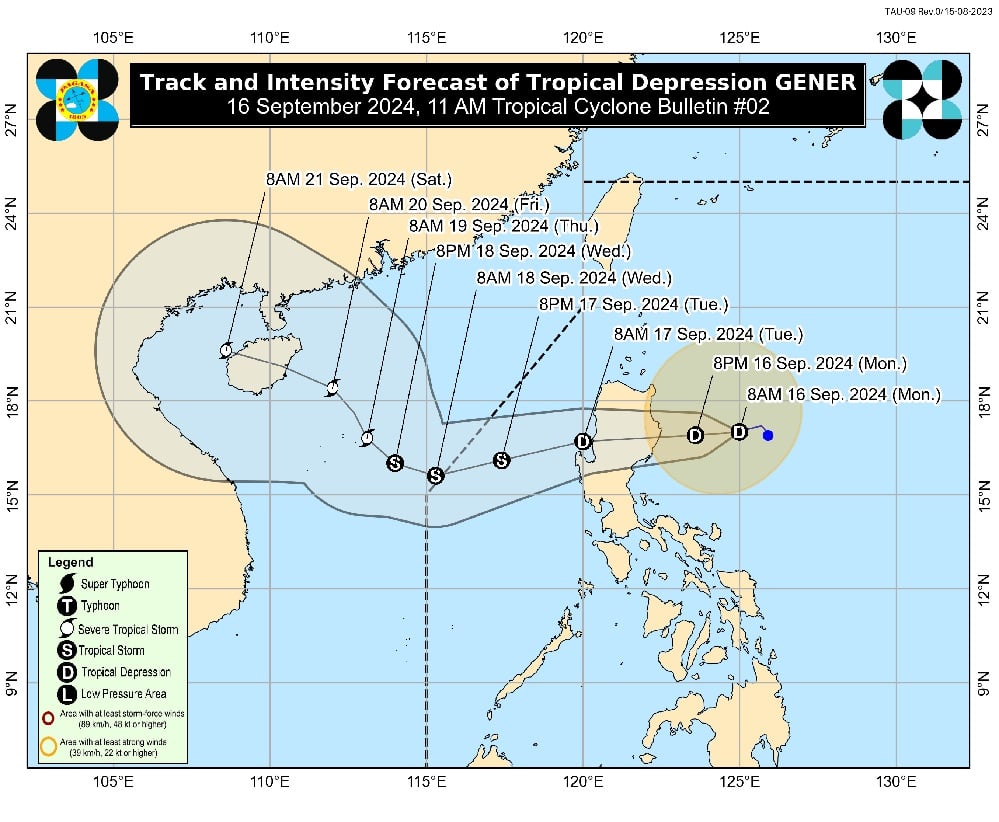
Article Bias: The article reports on the developments of Tropical Depression Gener, including its intensification, rainfall forecasts, and potential impacts on various regions in the Philippines, while maintaining a neutral tone focused on providing factual weather information without sensationalizing the situation.
Social Shares: 31
🔵 Liberal <-> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <-> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <-> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <-> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <-> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <-> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <-> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <-> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <-> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🔬 Scientific <-> Superstitious 🔮:
🤖 Written by AI:
AI Bias: Neutral information with a focus on factual reporting.
Article Bias: The article provides a factual report on the recent tropical storms affecting the Philippines, detailing their locations and expected impacts while remaining neutral and objective in tone.
Social Shares: 62
🔵 Liberal <-> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <-> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <-> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <-> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <-> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <-> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <-> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <-> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <-> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🔬 Scientific <-> Superstitious 🔮:
🤖 Written by AI:
AI Bias: Neutral reporting; focus on factual information.
Article Bias: The article provides an informative report on Typhoon Bebinca and its impacts, including forecasts and historical context, without exhibiting strong biases, though it mentions scientific links to climate change.
Social Shares: 0
🔵 Liberal <-> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <-> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <-> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <-> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <-> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <-> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <-> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <-> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <-> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🔬 Scientific <-> Superstitious 🔮:
🤖 Written by AI:
AI Bias: Limited by training data, may not fully capture nuances.
Article Bias: The article provides a factual account of Typhoon Bebinca and its impact in China, emphasizing the official reports on casualties, evacuation efforts, and the storm's progression without showcasing opinion or sensationalism.
Social Shares: 0
🔵 Liberal <-> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <-> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <-> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <-> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <-> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <-> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <-> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <-> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <-> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🤖 Written by AI:
AI Bias: Objective but limited by a focus on current events.
Article Bias: The article provides an informative report on Typhoon Bebinca and its impacts, including forecasts and historical context, without exhibiting strong biases, though it mentions scientific links to climate change.
Social Shares: 0
🔵 Liberal <-> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <-> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <-> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <-> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <-> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <-> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <-> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <-> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <-> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🔬 Scientific <-> Superstitious 🔮:
🤖 Written by AI:
AI Bias: Limited by training data, may not fully capture nuances.
Article Bias: The article provides an informative report on Typhoon Bebinca and its impacts, including forecasts and historical context, without exhibiting strong biases, though it mentions scientific links to climate change.
Social Shares: 0
🔵 Liberal <-> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <-> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <-> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <-> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <-> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <-> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <-> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <-> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <-> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🔬 Scientific <-> Superstitious 🔮:
🤖 Written by AI:
AI Bias: Limited by training data, may not fully capture nuances.
Meteorological Community
Article Bias: The article provides an informative report on Typhoon Bebinca and its impacts, including forecasts and historical context, without exhibiting strong biases, though it mentions scientific links to climate change.
Social Shares: 0
🔵 Liberal <-> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <-> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <-> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <-> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <-> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <-> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <-> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <-> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <-> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🔬 Scientific <-> Superstitious 🔮:
🤖 Written by AI:
AI Bias: Limited by training data, may not fully capture nuances.
Government Agencies
Article Bias: The article provides a factual account of Typhoon Bebinca and its impact in China, emphasizing the official reports on casualties, evacuation efforts, and the storm's progression without showcasing opinion or sensationalism.
Social Shares: 0
🔵 Liberal <-> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <-> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <-> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <-> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <-> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <-> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <-> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <-> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <-> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🤖 Written by AI:
AI Bias: Objective but limited by a focus on current events.
My Bias
Article Bias: The article provides an informative report on Typhoon Bebinca and its impacts, including forecasts and historical context, without exhibiting strong biases, though it mentions scientific links to climate change.
Social Shares: 0
🔵 Liberal <-> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <-> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <-> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <-> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <-> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <-> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <-> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <-> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <-> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🔬 Scientific <-> Superstitious 🔮:
🤖 Written by AI:
AI Bias: Limited by training data, may not fully capture nuances.
Article Bias: The article provides a factual account of Typhoon Bebinca and its impact in China, emphasizing the official reports on casualties, evacuation efforts, and the storm's progression without showcasing opinion or sensationalism.
Social Shares: 0
🔵 Liberal <-> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <-> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <-> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <-> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <-> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <-> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <-> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <-> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <-> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🤖 Written by AI:
AI Bias: Objective but limited by a focus on current events.
Article Bias: The article provides an informative report on Typhoon Bebinca and its impacts, including forecasts and historical context, without exhibiting strong biases, though it mentions scientific links to climate change.
Social Shares: 0
🔵 Liberal <-> Conservative 🔴:
🗽 Libertarian <-> Authoritarian 🚔:
🗞️ Objective <-> Subjective 👁️ :
🚨 Sensational:
📉 Bearish <-> Bullish 📈:
📝 Prescriptive:
🕊️ Dovish <-> Hawkish 🦁:
😨 Fearful:
📞 Begging the Question:
🗣️ Gossip:
💭 Opinion:
🗳 Political:
Oversimplification:
🏛️ Appeal to Authority:
🍼 Immature:
🔄 Circular Reasoning:
👀 Covering Responses:
😢 Victimization:
😤 Overconfident:
🗑️ Spam:
✊ Ideological:
🏴 Anti-establishment <-> Pro-establishment 📺:
🙁 Negative <-> Positive 🙂:
📏📏 Double Standard:
❌ Uncredible <-> Credible ✅:
🧠 Rational <-> Irrational 🤪:
🤑 Advertising:
🔬 Scientific <-> Superstitious 🔮:
🤖 Written by AI:
AI Bias: Limited by training data, may not fully capture nuances.


2024 © Helium Trades
Privacy Policy & Disclosure
* Disclaimer: Nothing on this website constitutes investment advice, performance data or any recommendation that any particular security, portfolio of securities, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person. Helium Trades is not responsible in any way for the accuracy
of any model predictions or price data. Any mention of a particular security and related prediction data is not a recommendation to buy or sell that security. Investments in securities involve the risk of loss. Past performance is no guarantee of future results. Helium Trades is not responsible for any of your investment decisions,
you should consult a financial expert before engaging in any transaction.
![]() Ask any question about this page!
Ask any question about this page!